Abstract: IgG4-related disease (RD) is characterized by lymphoplasmacytic infiltration enriched in IgG4-positive plasma cells and variable degrees of fibrosis with a characteristic storiform pattern. Since fibrosis is an important feature of IgG4-RD, we performed a prospective cohort study to evaluate the performance of 68Ga-fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI), a recently introduced PET agent targeting fibroblast activation protein, in IgG4-RD.
Methods: Twenty-six patients with IgG4-RD were recruited. All patients underwent both 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT. The positive rates of the PET/CT scans in the involved organs and the uptake values were compared.
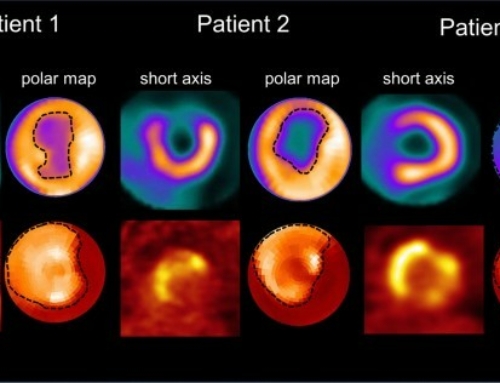
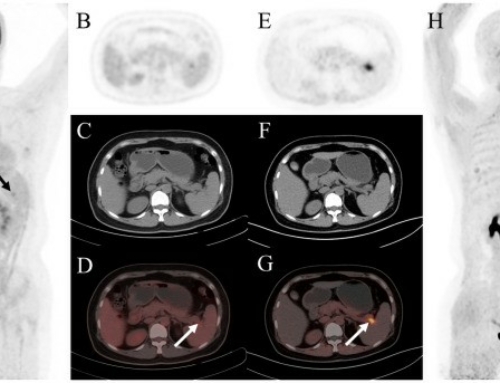
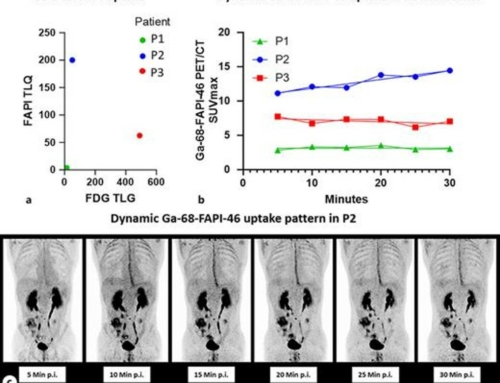
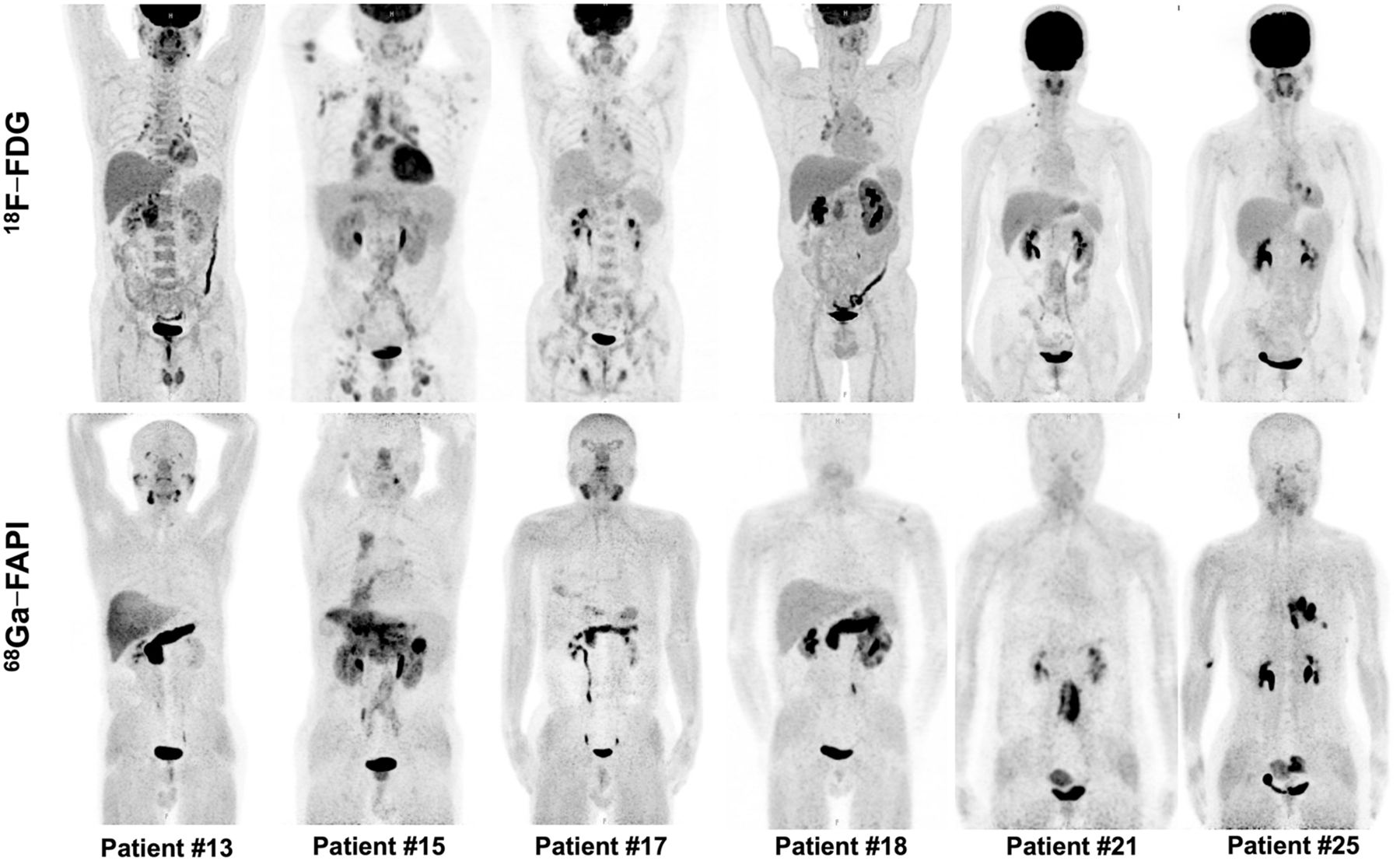
Results: In a total of 136 involved organs in the 26 patients, 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT additionally detected 18 (13.2%) involved organs in 13 (50.0%) patients, compared with 18F-FDG PET/CT. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT had a higher positive rate than 18F-FDG PET/CT in detecting involvement in the pancreas, bile duct/liver, and lacrimal gland. 68Ga-FAPI also demonstrated significantly higher uptake than 18F-FDG in the matched disease in the pancreas, bile duct/liver, and salivary gland (P < 0.01). However, lymph node involvement with flip-flop uptake of 18F-FDG did not accumulate 68Ga-FAPI.
Conclusion: 68Ga-FAPI might be a promising imaging agent for the assessment of IgG4-RD.
Affiliations:
- Department of Nuclear Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China.
- Beijing Key Laboratory of Molecular Targeted Diagnosis and Therapy in Nuclear Medicine, Beijing, China; and.
- Department of Rheumatology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China.
- Department of Nuclear Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China lifang@pumch.cn.

![Efficacy of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-PET as a non-invasive evaluation method of liver fibrosis](https://sofie.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/info.ibamolecular-500x383.png)
![Comparison of [99mTc]Tc-FAPI SPECT/CT and [18F]FDG PET/CT as predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy response in gastrointestinal cancer](https://sofie.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/info.ibamolecular-500x383.jpg)